Standard Vertex And Intercept Form
Intercept Form
The intercept form of the equation of a line is x/a + y/b = i. This is one of the important forms of equations of a line. Also, the sign of the intercepts in this equation helps united states of america to know the location of the line with respect to the coordinate axes. The intercept form of the equation of the line can exist understood equally the line which makes a right triangle with the coordinates axes, with the sides of lengths as 'a' units and 'b' units respectively.
Let u.s.a. now bank check the equation of intercept class, the graph of intercept grade, and the derivation of intercept form, from other forms of equations of a line.
| 1. | What is Intercept Course? |
| 2. | Graph of Intercept Course of Equation |
| 3. | Derivation of Intercept Class of Equation |
| 4. | Examples on Intercept Form |
| 5. | Practice Questions on Intercept Form |
| 6. | FAQs on Intercept Class |
What is Intercept Form?
The intercept course of the equation of a line has an equation x/a + y/b = 1, where 'a' is the x-intercept, and 'b' is the y-intercept. The ten-intercept is the shortest distance of the signal on the x-axis from the origin, where the line cuts the x-axis, and the y-intercept is the shortest distance of the point on the y-axis from the origin, where the line cuts the y-centrality. Too because the points, the line cuts the x-axis at the indicate(a, 0), and information technology cuts the y-axis at the point(0, b).
Intercept Form of Equation of a Line: x/a + y/b = one.
Here 10, y, are the variables in the equation, a, b, are the ten-intercept, and the y-intercept in the equation. This equation has a slope of -b/a.
Since this line cuts both the coordinate axes, information technology makes a right triangle with the coordinate axes, and the expanse of the right angled triangle is equal to the product of half of its intercepts 1/two · |ab|. Further, the intercept form of the equation of a line tin can be simplified and represented as the standard course of the equation of a line every bit bx + ay = ab.
Graph of Intercept Grade of Equation
The graph of intercept form cuts the coordinate axes at the two points on the ten-axis and the y-axis respectively. The 2 points are at distances of 'a' units and 'b' units from the origin, and on the x and y-axis respectively. Since the line cuts an intercept of 'a' units on the x-axis, it passes through the indicate (a, 0) on the ten-axis. and information technology cuts an intercept of 'b' units on the y-axis, it passes through the point (0, b) on the y-axis respectively.
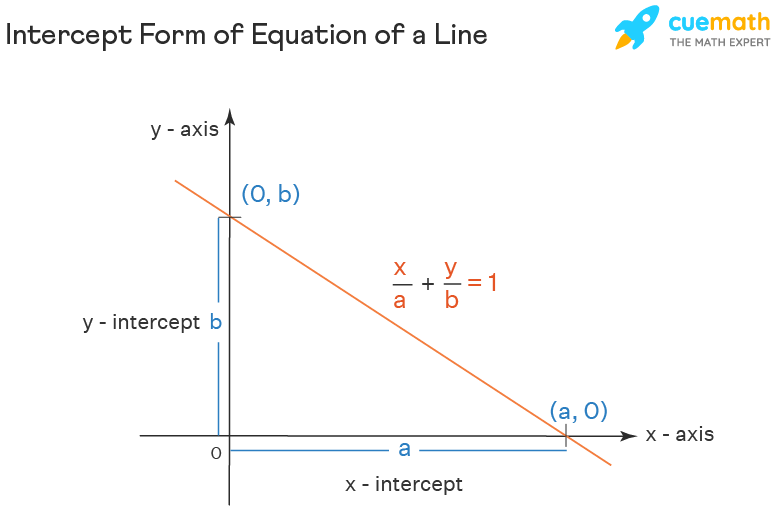
Derivation of Intercept Form of Equation
The intercept course of the equation of the line tin be derived from the other forms of equations of a line. Hither we derive the intercept form of the equation of the line from the two-point course of equation of a line.
2 Betoken Form
The two indicate class of equation of a line requires ii points on the line. The equation of a line passing through the ii-points (a, 0), and (0, b) can be found using the 2-betoken form of the equation of a line. The equation of the line passing through the 2 points (a, 0), and (0, b) respectively is as follows.
y - 0 = (b - 0)/(0 - a).(x - a)
y = b/-a.(x - a)
-ay = b(x - a)
-ay = bx - ab
ab = bx + ay
bx + ay = ab
(bx + ay)/ab = 1
bx/ab + ay/ab = 1
ten/a + y/b = one
Important Notes on Intercept Form:
The following points aid in clearly understanding the details of the intercept form of the equation of a line.
- The intercept form of the equation of a line is ten/a + y/b = one.
- The intercept course of the equation of a line makes the 10-intercept of 'a' units, and the y-intercept of 'b' units.
- Based on the sign of the intercepts we can detect the quadrants through which the line passes through.
- The intercept course of the equation of a line makes a right triangle with the coordinate axes, and the area of this right triangle is 1/2 · |ab|.
☛ Related Topics:
The following related topics are helpful for a amend understanding of the intercept grade of the equation of a line.
- Coordinate Geometry
- Coordinate Plane
- Cartesian Coordinates
- y = mx + b
Examples on Intercept Form
go to slidego to slidego to slide

Accept questions on basic mathematical concepts?
Become a problem-solving champ using logic, not rules. Learn the why behind math with our certified experts
Volume a Free Trial Class
Practice Questions on Intercept Course
become to slidego to slide
FAQs on Intercept Form
What is Intercept Form of Equation of a Line?
The Intercept Class of Equation of a Line is of the Form ten/a + y/b = 1. Here 'a' is the x-intercept, and 'b' is the y-intercept. The value of 'a' is the distance from the origin, and on the 10-axis, at which this line cuts the x-axis, and the value of 'b' is the distance from the origin, and on the y-centrality, at which this line cuts the y-axis. The signs of these intercepts helps u.s. to know the quadrants through which this line is passing.
What Can be Derived From the Intercept Form of Equation of A Line?
The intercept form of the equation of the straight line helps u.s. to derive two important aspects. Firstly, the intercept form of equation of line ( x/a + y/b = i), helps u.s. in knowing the x-intercept and the y-intercept of the line. Secondly, based on the signs of the intercepts, we can discover the quadrant through which this line passes.
How To Catechumen Intercept Course to Standard Form of Equation of a Line?
The intercept form of the equation of the line can be easily transformed into the standard grade of the equation of a line. The intercept grade of the equation of the line is x/a + y/b = i, and the standard form of the equation of the line is ax + by + c = 0. The steps of transformation from intercept form to standard form is as follows.
x/a + y/b = ane
(bx + ay)/ab = i
bx + ay = ab
This above-derived equation of a line is of the class ax + by + c = 0, and information technology represents the standard equation of a line.
What Are the Other Forms of Equations of a Line, Similar to Intercept Course?
The other forms of equations of a line, similar to intercept form, are as follows.
- Point Gradient Form: y - yone = m(x - xi).
- Ii Point Form: y - yane = (y2 - y1)/(tenii - xone) · (ten - x1)
- Slope Intercept Form: y = mx + c
- Intercept Form: 10/a + y/b = 1
- Normal Course: ten cos θ + y sin θ = P
Standard Vertex And Intercept Form,
Source: https://www.cuemath.com/geometry/intercept-form/
Posted by: shropshiregustanotests.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Standard Vertex And Intercept Form"
Post a Comment